Understanding Glutamine
Glutamine is a vital amino acid that plays a significant role in various metabolic processes within the body. As the most abundant amino acid in the bloodstream, it is primarily stored in the muscles and essential for muscle repair and growth. During times of stress, such as illness or intense exercise, the body may require additional glutamine to maintain its functions.

Sources of Glutamine
There are various dietary sources of glutamine. Natural, high-protein foods such as meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, and legumes are excellent sources. Additionally, glutamine can be found in some vegetables, including spinach, cabbage, and broccoli. For those looking to enhance their glutamine intake, supplements are also widely available, particularly in powder form, which can be easily incorporated into smoothies or protein shakes.
Benefits of Glutamine
Several studies have examined the benefits of glutamine for both athletic performance and overall health. Research indicates that glutamine may help in muscle recovery after workouts, reduce muscle soreness, and improve overall performance. Beyond fitness, glutamine has also been studied for its potential role in gut health and the immune system, suggesting that it supports the integrity of the intestinal lining and aids in the body’s defense against infections.
In conclusion, glutamine is a multifaceted amino acid with numerous benefits, particularly for athletes and individuals under physical stress. Incorporating glutamine-rich foods or supplements into your diet can be advantageous for recovery and overall well-being.
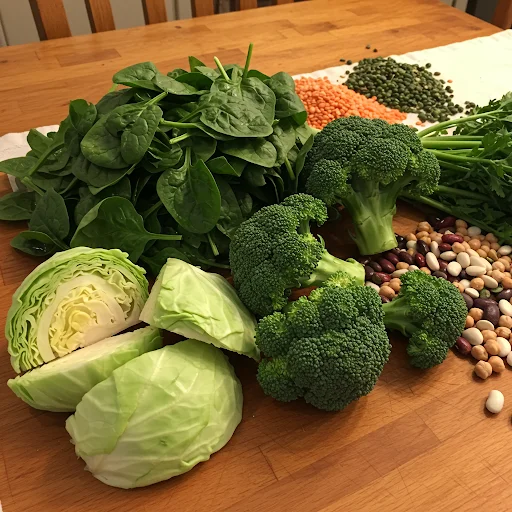

How I Get my Glutamine From My Diet
My plant-based diet, which includes spinach, cabbage, broccoli, and legumes, provides me with a steady supply of glutamine.