The Origins of Frankincense: A Historical Perspective
Frankincense, a resin obtained from the Boswellia tree, boasts a profound historical significance that dates back thousands of years. Its origins are rooted in ancient civilizations, most notably in regions such as Egypt, Greece, and the Arabian Peninsula. Known as ‘olibanum’ in some cultures, it has been a critical commodity, revered for its aromatic qualities and therapeutic uses.

In ancient Egypt, frankincense was cherished as a luxurious item and played an integral role in various spiritual practices. It was often burned in temples during religious rituals and was commonly associated with the embalming process, symbolizing purification and holiness. The Egyptians linked frankincense to the divine, frequently using it to honor their gods, and it became a staple in their medicinal practices. The archaeological discoveries have revealed immense quantities of frankincense in ancient burial sites, indicating its value as an offering for the afterlife.
The Greeks also embraced the properties of frankincense, which was celebrated for its medicinal benefits. They utilized it to treat an array of ailments, ranging from respiratory issues to digestive disorders. The ancient physician Dioscorides documented its various uses, further establishing its significance in classical pharmacology. In addition, the Greeks were instrumental in the trade of frankincense, linking the Arabian Peninsula with Europe, thus enhancing the economic and cultural exchanges between these regions.
Meanwhile, in the Arabian Peninsula, frankincense was woven into the very fabric of daily life and spirituality. It was utilized not just in trade, where it was considered one of the “gifts” of the East, but also in religious practices, reflecting the importance of incense in cultural rituals. Through centuries of history, frankincense has transcended beyond a mere commodity to become a sacred element that significantly shaped spiritual beliefs and medicinal practices across various cultures.
Forms of Frankincense: Options for Every Use
Frankincense, derived from the resin of the Boswellia tree, is available in various forms that cater to different needs and preferences. Each form is processed uniquely, offering a distinct set of benefits and applications. Understanding these forms can help consumers make informed choices for their particular uses, whether they seek therapeutic benefits, skincare solutions, or health supplements.

The most common form is frankincense essential oil, which is extracted through steam distillation of the resin. This oil captures the essence of frankincense, making it suitable for aromatherapy. It is renowned for its calming properties and is often used in diffusers or blended with carrier oils for topical application. Essential oil users appreciate its ability to enhance meditation practices and promote overall well-being.

Frankincense resin is another popular form that is typically used in incense. This raw form of the plant is harvested and can be burned to release aromatic compounds. The resin’s anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties have led to its use in traditional medicine practices. Burning frankincense can create a relaxing environment, making it ideal for spiritual rituals and stress relief.

For those who prefer ingestible forms, frankincense capsules and tinctures are available. These supplements typically contain powdered resin or extract, offering convenience for daily consumption. Capsules are easy to incorporate into a routine, while tinctures, which involve alcohol-based extraction, are more concentrated and can be diluted in water or taken directly. These forms are particularly advantageous for individuals seeking specific health benefits, such as joint support or enhanced respiratory function.
Ultimately, the diversity of frankincense forms ensures that there is a suitable option for everyone. Selecting the right type depends on individual preferences and intended use, whether for therapeutic, cosmetic, or health-related purposes.
Health Benefits of Frankincense: A Closer Look
Frankincense, derived from the resin of the Boswellia tree, has been utilized for centuries, celebrated in both ancient cultures and modern therapeutics. Its multifaceted health benefits primarily stem from its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and calming properties, making it a valuable addition to holistic health practices. Studies have shown that the active compounds in frankincense oil, specifically boswellic acids, exhibit potent anti-inflammatory effects. These characteristics are particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from chronic inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, where frankincense may help reduce swelling and joint pain, thereby enhancing overall mobility and quality of life.
Moreover, frankincense has demonstrated significant antimicrobial properties. Research indicates that the essential oil exhibits activity against various strains of bacteria and fungi, suggesting its potential as a natural antiseptic. Incorporating frankincense in wellness routines can support a robust immune system, thereby decreasing susceptibility to infections and promoting overall health. Additionally, the calming effects attributed to frankincense play a crucial role in mental well-being. Its aromatic profile has been shown to reduce stress and anxiety levels, fostering a sense of tranquility and enhancing mood. Inhaling frankincense through aromatherapy or using it in meditation practices can create an environment conducive to relaxation and mental clarity.
Furthermore, clinical studies have supported these traditional applications, revealing not only subjective benefits reported by users but also objective improvements in health metrics. For instance, certain research suggests that frankincense may assist in reducing cortisol levels, the body’s primary stress hormone. As modern science continues to validate the healing properties of frankincense, integrating it into daily health routines shows promise for enhancing physical and mental well-being. Therefore, understanding and harnessing these benefits can lead to better health outcomes and improved quality of life.
Clinical Studies on Frankincense: Research and Evidence
Frankincense, derived from the resin of Boswellia trees, has been the subject of numerous clinical studies aimed at evaluating its therapeutic potential and health benefits. Recent research has focused on various health conditions, including inflammatory disorders, respiratory issues, and cancer. Notable studies have employed diverse methodologies such as randomized controlled trials (RCTs), cohort studies, and systematic reviews to examine the efficacy of frankincense extracts, particularly boswellic acids, in clinical settings.
One prominent study published in a peer-reviewed journal explored the effects of boswellic acid on patients with osteoarthritis. This trial involved a sample size of 150 participants over a six-month period and demonstrated a significant reduction in pain and improvement in mobility compared to the placebo group. The outcomes were attributed to the anti-inflammatory properties of boswellic acids, which may inhibit specific inflammatory pathways within the body.
Additionally, studies have investigated the use of frankincense in managing respiratory conditions. One exploratory clinical trial involving patients with asthma indicated that inhalation of frankincense essential oil led to reduced airway inflammation and improved lung function metrics. These findings suggest that frankincense could be a complementary treatment for individuals suffering from chronic respiratory ailments.
However, it is crucial to recognize the limitations present in current frankincense research. Many studies have relatively small sample sizes and varying methodologies, which can impact the generalizability of the findings. Moreover, while some evidence supports the health claims regarding frankincense, further comprehensive and larger-scale studies are necessary to establish definitive conclusions about its efficacy and safety.
This compilation of clinical studies emphasizes the need for continued research on frankincense, as it may hold significant promise in alternative medicine and the management of various health conditions.
Topical Frankincense Oil Application and Remission of Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Personal Account
In June 2019, a small lesion appeared on my left shin. Over the following months, it rapidly increased in size, raising concerns about potential skin cancer. In early September, a physician diagnosed the lesion as suspected squamous cell carcinoma. Due to its proximity to the shin bone, surgical removal by a dermatologist was recommended. The earliest available appointment was scheduled for mid-November, over six weeks later. Given the rapid growth of the lesion, I sought immediate intervention.
To explore potential options for slowing the lesion’s progression while awaiting my dermatology appointment, I conducted online research. My search led me to PubMed, where I discovered several studies on Boswellia serrata (frankincense). Notably, one article detailed a clinical trial demonstrating positive results in treating skin cancer with frankincense essential oil. Inspired by this research, I acquired frankincense oil from Amazon.
The clinical trial utilized a 1:20 dilution of frankincense oil in jojoba carrier oil. However, I opted for a 1:1 dilution, a significantly higher concentration. This resulted in mild irritation to the surrounding healthy skin, but I continued twice-daily applications. Approximately two weeks into the treatment, I observed a noticeable change: the lesion appeared to be healing from within. Eventually, the lesion detached, leaving a small depression. By the time of my dermatology appointment, the site was fully healed, with only a slight discoloration remaining. The dermatologist confirmed the initial diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma and verified the complete resolution of the lesion.
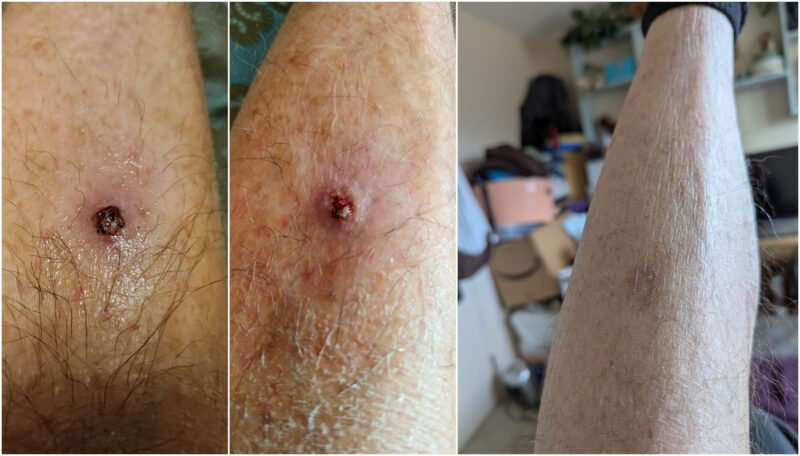
I am not advising others to follow my protocol, as there is no guarantee of achieving the same outcome. While it was effective for me, and scientific research indicates some positive results, I strongly recommend consulting with a healthcare professional. At a minimum, conduct thorough personal research and begin with a significantly diluted solution. The three attached photos illustrate the tumor at three stages: initial presentation, midway through treatment, and the final result.

