What is Lysine?
Lysine, an essential amino acid, plays a pivotal role in various physiological processes. As one of the building blocks of proteins, lysine is indispensable for the synthesis of proteins in the body. Unlike non-essential amino acids, which can be synthesized by the body, lysine must be obtained through dietary sources, making it crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. The classification of lysine as an essential amino acid highlights its importance in human nutrition.
The primary biochemical functions of lysine include its involvement in collagen production, which is vital for maintaining skin elasticity and structural integrity in connective tissues. This amino acid also plays a significant role in the synthesis of enzymes, hormones, and antibodies, which are integral to various metabolic processes and immune function. Furthermore, lysine has been shown to enhance calcium absorption in the body, promoting bone health and reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
In addition to its structural and functional roles, lysine is known for its potential therapeutic benefits. Research suggests that lysine may help in the management of herpes simplex virus outbreaks by reducing the severity and frequency of symptoms. Moreover, it may contribute to improved muscle recovery and decreased soreness after intense exercise, making it particularly beneficial for athletes and individuals engaged in regular physical activity.
As a vital amino acid, lysine is present in various food sources, including meat, dairy, legumes, and certain grains. To ensure adequate intake, individuals need to incorporate these foods into their diet, especially those who follow vegetarian or vegan lifestyles, as plant-based sources may provide lower concentrations of lysine compared to animal products.
Forms of Lysine

Lysine is an essential amino acid that exists in different forms, the most notable being L-lysine and D-lysine. L-lysine, the biologically active form of this amino acid, plays a critical role in protein synthesis and the overall functioning of the human body. It is readily absorbed and utilized for various physiological processes, such as promoting collagen production and supporting immune functions. In contrast, D-lysine does not participate in these processes and is often considered inactive from a biological perspective.

The primary focus should be on the availability of L-lysine, as this is the form that provides health benefits when consumed. L-lysine can be found in various dietary sources such as meat, dairy products, eggs, and certain legumes, but for those who struggle to meet their daily requirements through diet alone, lysine supplements can offer a practical solution. Lysine supplements come in several forms, including powders and capsules, allowing individuals to choose based on their preferences and lifestyle.
When considering lysine supplementation, it is essential to examine the intended use and recommended dosages. Powders offer versatility, allowing users to mix with beverages or foods, making it easier to adjust the dosage according to individual needs. Capsules, on the other hand, provide convenience for on-the-go consumption. Generally, the recommended dosage can vary depending on factors such as age and specific health conditions. Dosages often range from 500 mg to 3,000 mg per day, though it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen.
Understanding the forms of lysine available through diet and supplements is crucial for individuals looking to harness the benefits of this essential amino acid. By focusing on L-lysine and selecting the appropriate supplementation form, individuals can optimize their intake effectively.
Dietary Sources of Lysine
Lysine, an essential amino acid, plays a critical role in various physiological functions, including protein synthesis, hormone regulation, and immune system support. It is important to ensure an adequate intake of lysine through dietary sources, which can be categorized into animal-based and plant-based foods.
Animal-based foods are among the most excellent sources of lysine due to their high protein content. Meat, especially red meats like beef and lamb, provides a significant amount of lysine, as do poultry products such as chicken and turkey. Fish is another important source, with varieties such as cod and salmon containing substantial levels of this essential amino acid. Additionally, eggs and dairy products, including milk, yogurt, and cheese, are particularly rich in lysine and contribute to balanced nutrition. These foods are crucial for individuals who consume a primarily omnivorous diet and can help meet the daily lysine requirements without difficulty.
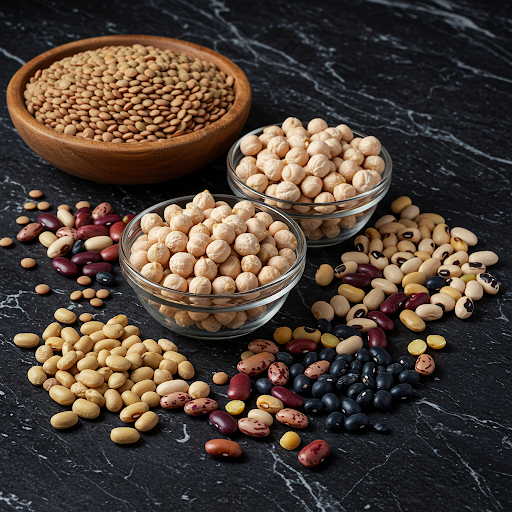

For vegetarians and vegans, obtaining sufficient lysine may require more attention, as many plant-based foods contain lower amounts of this amino acid. However, several plant sources can serve as effective lysine providers. Legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and beans are excellent choices, as they offer both protein and lysine. Soy products, including tofu and edamame, are particularly notable for their high lysine content and versatility in culinary applications. Furthermore, certain nuts and seeds, such as pistachios and pumpkin seeds, can contribute to lysine intake, although they should be complemented with other protein sources to ensure a well-rounded amino acid profile.
Incorporating a variety of these lysine-rich foods into the diet is essential for individuals of all dietary preferences. By being mindful of the sources and combinations of foods consumed, one can effectively meet their lysine needs while promoting overall health and well-being.
Health Benefits of Lysine
Lysine, an essential amino acid, plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, making it important for overall health. One of the primary benefits of adequate lysine intake is its supportive role in immune health. By participating in the production of antibodies and aiding in the formation of collagen, lysine contributes significantly to the body’s defense mechanisms against pathogens.
Moreover, lysine is known to enhance calcium absorption, which is vital for maintaining bone health and density. This process not only supports the skeletal system but also emphasizes lysine’s role in preventing osteoporosis. In addition to these benefits, lysine is beneficial for muscle recovery. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts often rely on lysine to expedite the repair of muscle tissues following intense exercise—this recovery ensures improved performance and reduced muscle soreness.
Another noteworthy aspect of lysine is its involvement in hormone and enzyme production. Hormones such as insulin, which regulate critical metabolic processes, require lysine for proper synthesis. This amino acid also plays a role in synthesizing enzymes crucial for various biochemical pathways, showcasing its versatility in promoting metabolic health.
Beyond these physiological functions, lysine has potential psychological benefits, including anxiety reduction and managing episodes related to the herpes simplex virus. By modulating neurotransmitter activity, lysine may help alleviate anxiety symptoms, providing a natural avenue for support. Furthermore, research indicates that lysine supplementation can reduce the frequency and severity of herpes outbreaks, making it a potential adjunct therapy for those affected by this condition.
Why I Take Lysine
I take a teaspoon of lysine powder every day to help prevent the recurrence of shingles and cold sores. This seems to be working, as I have been free of both for many years now.
Despite its numerous benefits, it is essential to consider potential side effects or contraindications associated with lysine supplementation. While generally safe when taken in appropriate amounts, some individuals may experience gastrointestinal discomfort or allergic reactions in rare cases. Consequently, maintaining balanced lysine levels through a diet rich in protein sources, including meat, dairy, and legumes, is advisable for optimal health.

